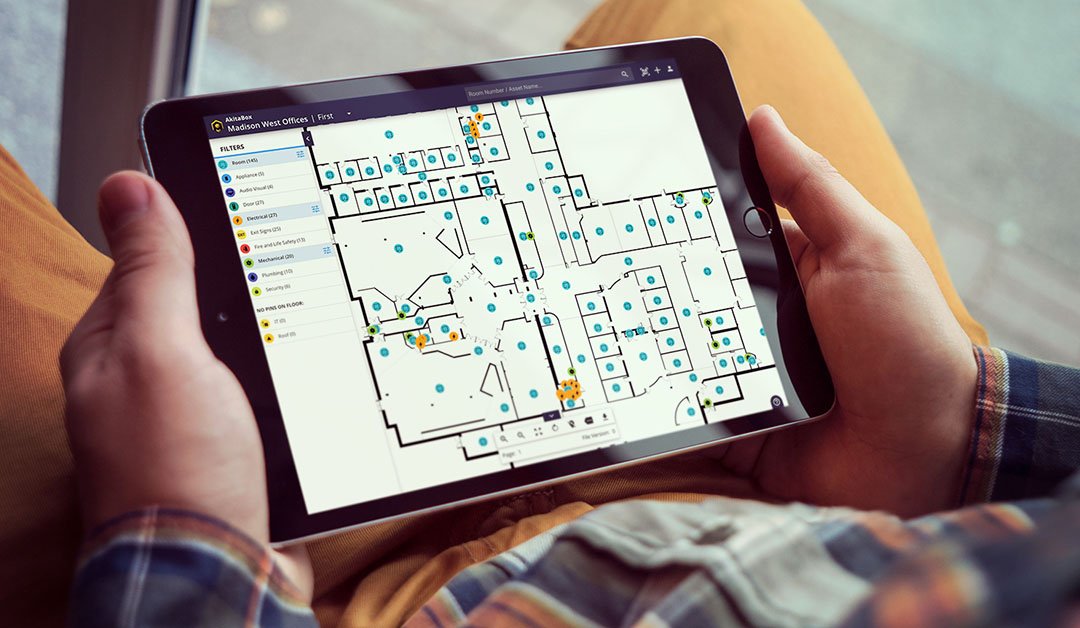
Building Management System (BMS)
A Building Management System (BMS), also known as a Building Automation System (BAS) or Building Control System (BCS), is a centralized system that monitors and controls various building services and systems to ensure efficient operation, comfort, safety, and security within a facility. BMSs are commonly used in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, hospitals, educational institutions, and large residential complexes. They integrate and automate the management of various building subsystems, including HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), lighting, electrical, fire and life safety, security, and access control. Here’s an overview of the typical components and types of BMS:
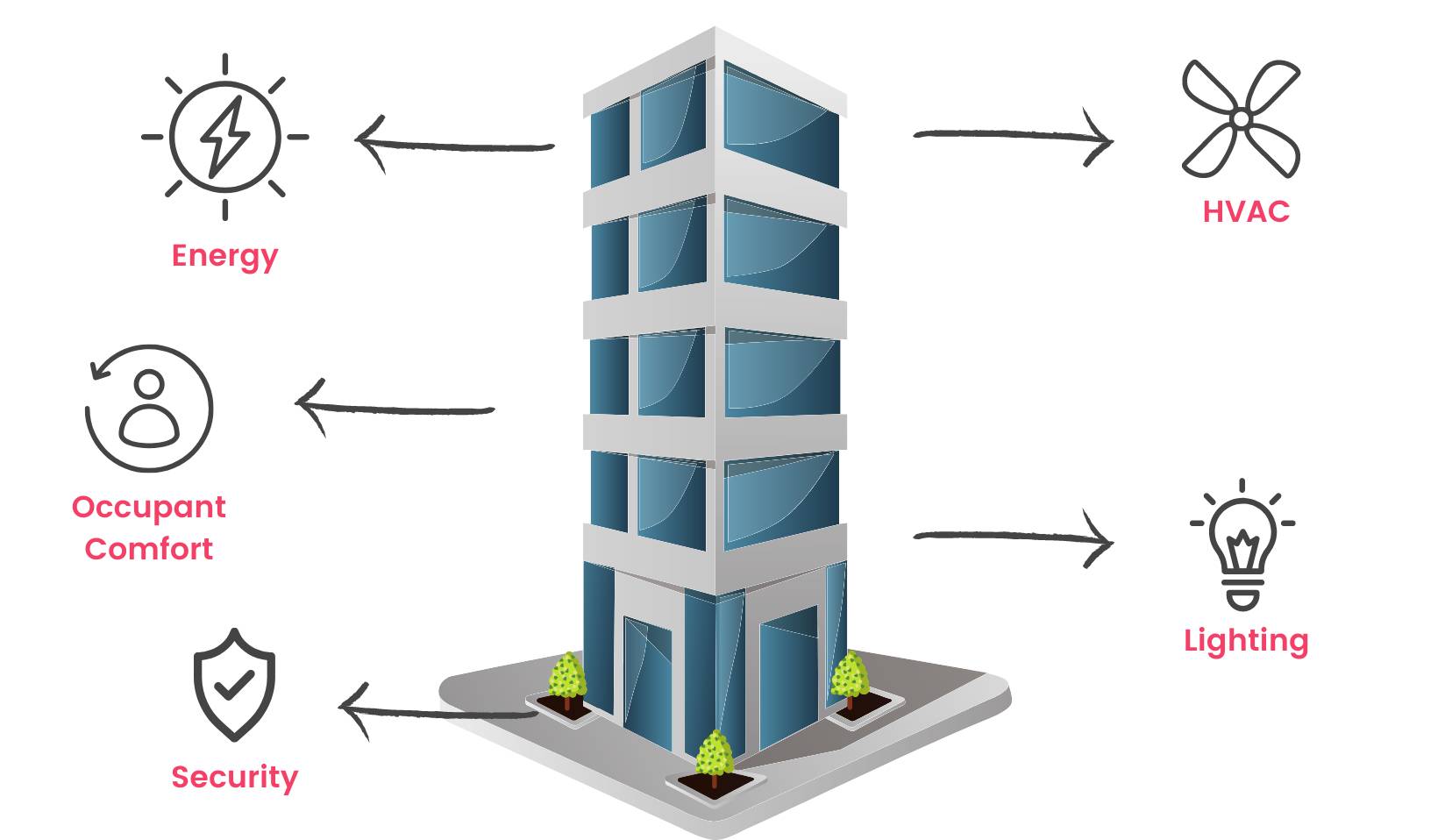
Components of a Building Management System
- Sensors and Detectors: Sensors and detectors are installed throughout the building to monitor parameters such as temperature, humidity, occupancy, air quality, smoke, and carbon monoxide levels.
- Controllers: Controllers receive data from sensors and detectors and send control signals to actuators and devices to regulate building systems. They may be programmable logic controllers (PLCs), microcontrollers, or specialized BMS controllers.
- Actuators: Actuators are devices that respond to control signals from the BMS to adjust system parameters. Examples include valves, dampers, motors, relays, switches, and pumps.
- User Interface: The user interface allows building operators and managers to monitor system performance, view alarms and alerts, adjust setpoints, and control building functions. User interfaces may include graphical user interfaces (GUIs), touchscreens, web interfaces, and mobile apps.
- Communication Network: A communication network connects BMS components, allowing data exchange and remote access. Common communication protocols include BACnet, Modbus, Lon Works, and Ethernet/IP.
Types of Building Management Systems
- HVAC Control Systems: HVAC control systems regulate heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to maintain indoor comfort conditions while optimizing energy usage. They monitor temperature, humidity, air flow, and occupancy to adjust HVAC equipment operation accordingly.
- Lighting Control Systems: Lighting control systems manage artificial lighting to enhance energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and productivity. They may include dimming, scheduling, occupancy sensing, and daylight harvesting features.
- Energy Management Systems (EMS): EMSs optimize energy consumption and reduce utility costs by monitoring and controlling energy usage across multiple building systems. They may incorporate demand response, load shedding, and energy conservation strategies.
- Fire and Life Safety Systems: BMSs integrate fire detection, alarm, and suppression systems to enhance building safety and facilitate emergency response. They monitor smoke and heat detectors, control fire dampers, and activate fire alarm notification devices.
- Security and Access Control Systems: Security and access control systems manage building access, surveillance, and intrusion detection to safeguard occupants and assets. They control door locks, security cameras, motion sensors, and alarm panels.
- Elevator and Escalator Control Systems: BMSs coordinate elevator and escalator operation to optimize traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and enhance passenger safety and convenience.
- Water Management Systems: Water management systems monitor and control water usage, distribution, and conservation measures within a building, including plumbing fixtures, irrigation systems, and water treatment equipment.